Command Line Interface (CLI)
Although we have been interacting with the interface so far, the interface is not the only way to use Windows.
We can also interact using only the keyboard.
Command Prompt (cmd)
Command Prompt is a command-line interpreter in Windows. It allows users to manage their computers through a text-based interface.
It enables users to perform file management, system configuration, network settings, program execution, and other system tasks. Commands can take parameters when executed.
For example, to find out the list of running processes:
tasklistTo find out the name of the currently logged-in user:
whoamiTo clear the screen:
cls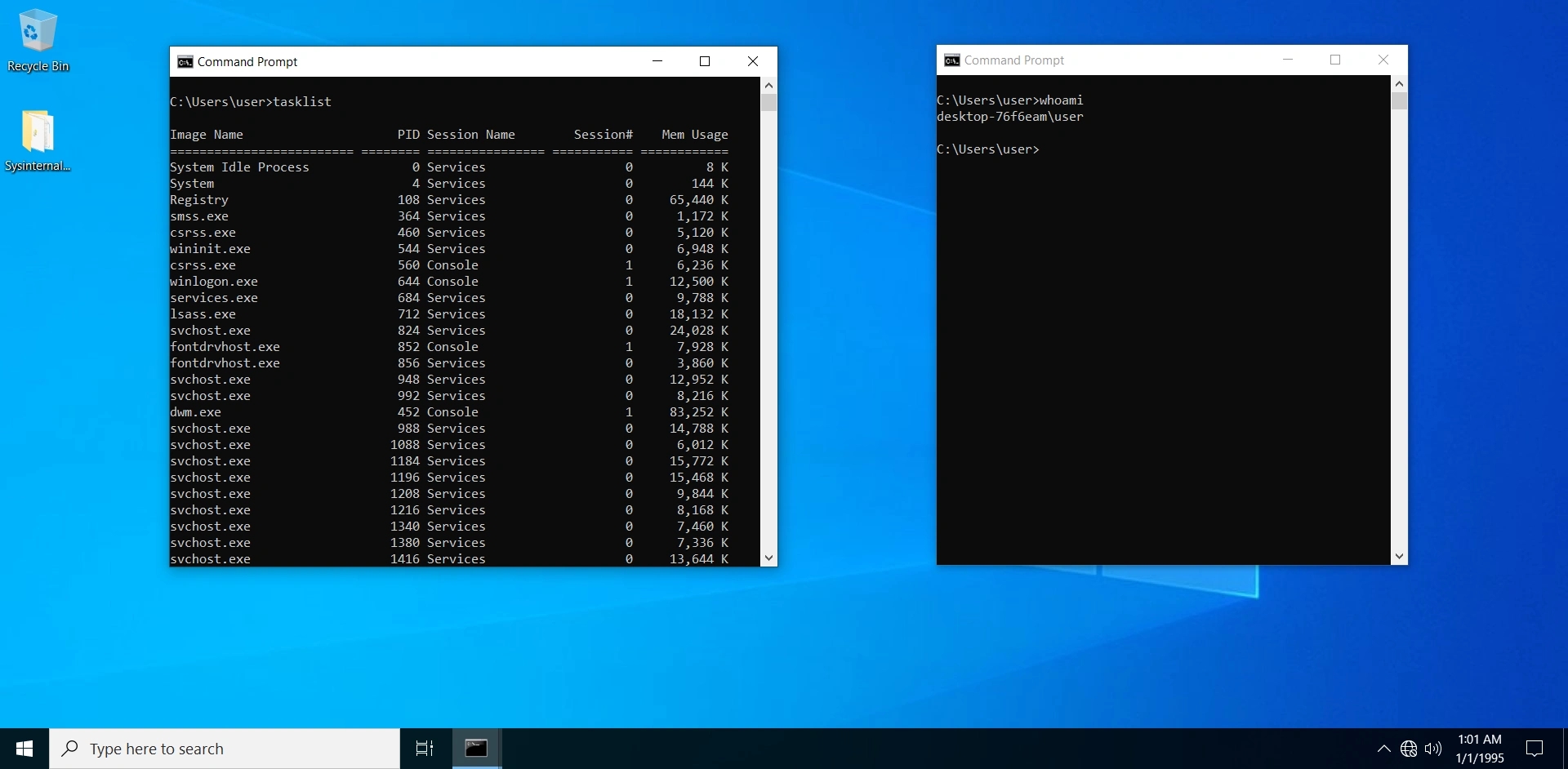
PowerShell
PowerShell is a command-line interface and scripting language developed by Microsoft for the Windows operating system.
It provides an advanced command-line interface and scripting environment. It has more advanced features than the classic Command Prompt (CMD) and can be used to automate many different tasks.
PowerShell is a command processor based on the .NET Framework. This means users can access .NET Framework libraries and manipulate .NET objects using PowerShell scripts, making PowerShell somewhat object-oriented.
PowerShell uses small, single-purpose commands called cmdlets. These cmdlets are used to perform various system management tasks. Additionally, users can create their own scripts in PowerShell and automate complex processes through PowerShell script files (*.ps1 extension).
Microsoft recommends using PowerShell instead of Command Prompt, and it is backward compatible with Command Prompt.
Now, let's examine commands that can be used for troubleshooting with PowerShell.
To find out the network address settings of the computer:
To see the settings that can be used with the command:
Last updated